Did you know that businesses that invest in multilingual websites see a staggering 70% boost in conversion rates?
However, going global means more than just translating your content.
It’s about using multilingual SEO strategies to ensure your brand is discoverable and relevant in every market you target.
In this article, we’ll explore 5 multilingual SEO best practices that will help you break language barriers and capture new audiences effectively. Let’s get started!
What is Multilingual SEO?
Multilingual SEO is the process of optimizing your website to ensure it is accessible and visible to audiences who speak different languages.
Adapting your content to multiple languages allows you to connect with users who are searching in their native languages.
While English is widely spoken, only about 50% of internet users communicate in it.
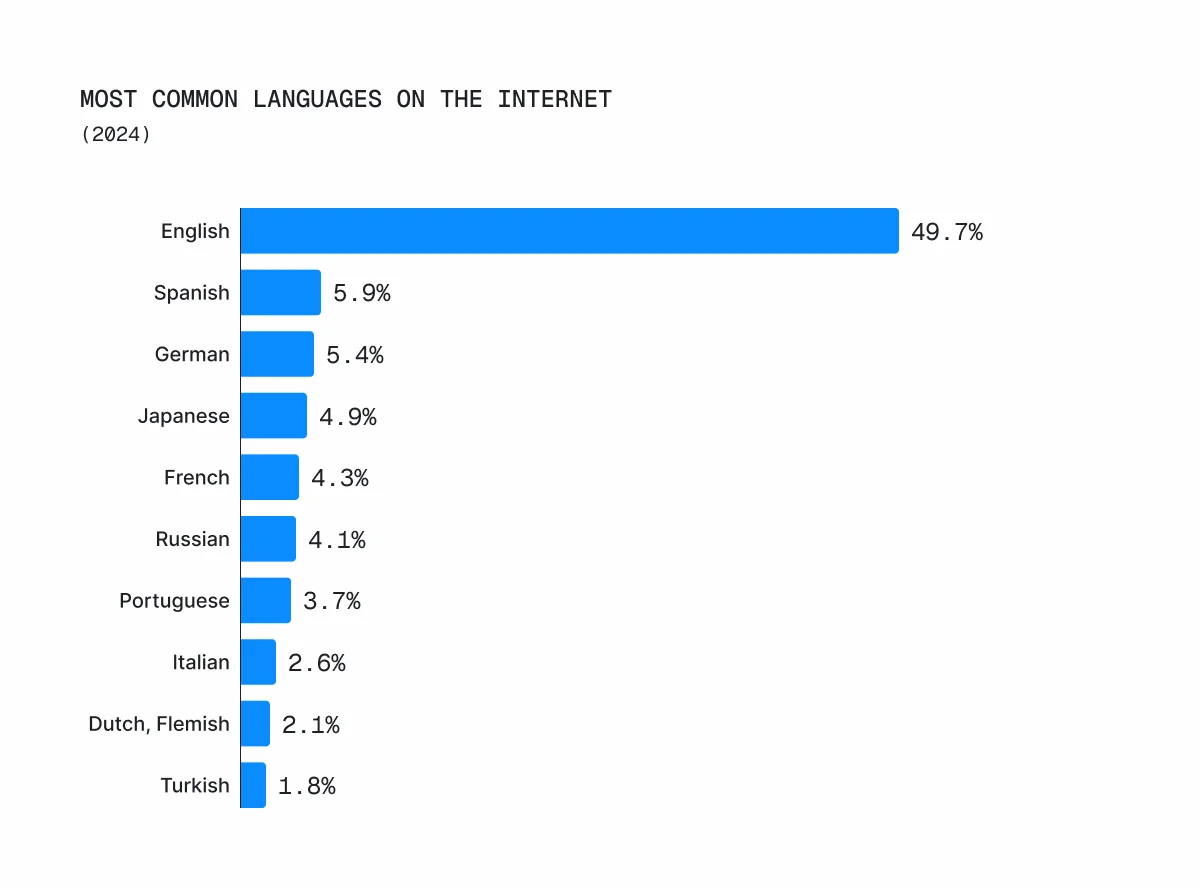
This makes multilingual SEO a valuable strategy for reaching a broader audience and maximizing your online visibility.
For example, translating your English content into French to connect with search engine users in France is a practical example of multilingual SEO in action.
Benefits of Multilingual SEO
Optimizing your website for multiple languages can unlock significant advantages for your business.
Here are five key multilingual SEO benefits:
- Gives you a competitive edge – Multilingual SEO allows you to outpace competitors by reaching diverse language groups across the globe.
It helps you tap into new markets and drive global traffic to your website.
- Improves overall SEO ranking – Translated versions of your site boost your chances of appearing on search engines’ first pages.
Search engines treat all translated pages as part of one website, creating a compound effect that increases traffic and enhances your site’s ranking.
- Helps you reach specific audiences – Multilingual SEO involves tailoring your site to the native languages of particular audiences.
With geo-targeting, you can effectively connect with local audiences and cater to their unique needs.
- Supports consistent business growth – A multilingual website helps build global brand awareness, informing international audiences about your products and services. This drives traffic, increases revenue, and ensures sustained growth over time.
- Expands access to local search engines – Many countries, like China and Japan, rely on search engines unique to their regions, such as Baidu or Yahoo! Japan.
Multilingual websites allow you to tap into these local platforms, significantly expanding your reach and traffic potential.
5 Multilingual SEO Best Practices to Boost Your Global Visibility
1. Identify Your Target Markets
To expand your business internationally, focus on countries or regions with strong demand for your products or services.
Once you’ve selected your target markets, localize your online presence by translating your website content into the dominant languages of those countries.
For example, for Brazil, ensure your content is available in Portuguese.
To identify promising markets, you need to:
- Study market geography – Analyze data to uncover regions with strong demand for your industry or product category.
Use tools like Google Trends, Statista, or Ahrefs to analyze demand trends and identify regions with high traffic potential in your niche.
- Evaluate competitor success – Research where your competitors are gaining traction. Platforms such as SimilarWeb, SEMrush, or Ahrefs can help you track and analyze competitor performance.
- Assess audience overlap – Identify countries where your competitors’ audience aligns with yours.
Google Analytics, or YouGov, can help you identify shared audience interests and overlap between your market and your competitors.
2. Use Location-Specific Keywords
Keywords aren’t universal, so it’s essential to conduct specific keyword research for each language and region your website targets.
Location-based keywords go beyond language, so simply translating them won’t be enough to capture the nuances of local search behavior.
Even within the same language, different regions may use distinct terms. For example:
- In the US, people might search for “apartments,” while in the UK, they’re more likely to search for “flats.”
- Similarly, a term like “vacation” in the US is commonly replaced with “holiday” in the UK.
Here are the crucial steps for conducting keyword research:
- Identify seed keywords – Brainstorm broad phrases or single words related to your business in the country-specific language.
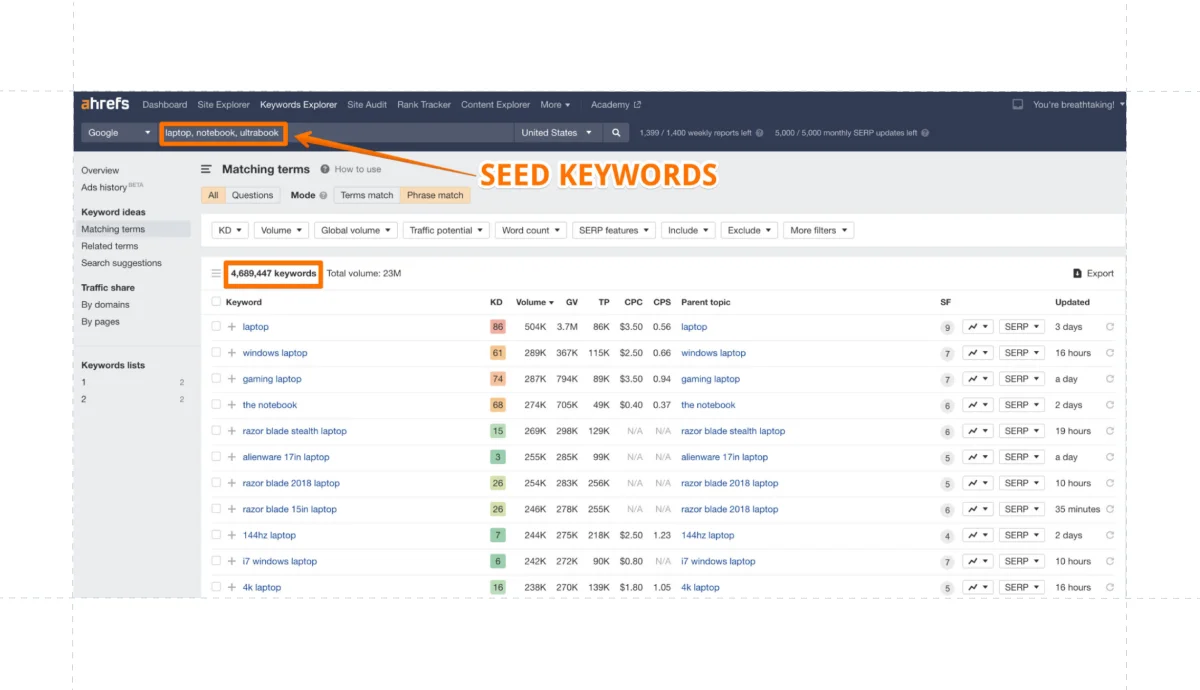
To ensure accuracy and cultural relevance, work with a native speaker or qualified translator during this process.
- Use keyword research tools – Use tools like Semrush and Ahrefs to generate related keyword ideas based on your seed keywords.
To refine your list, input keywords, select the target country, and analyze metrics such as search volume and keyword difficulty.
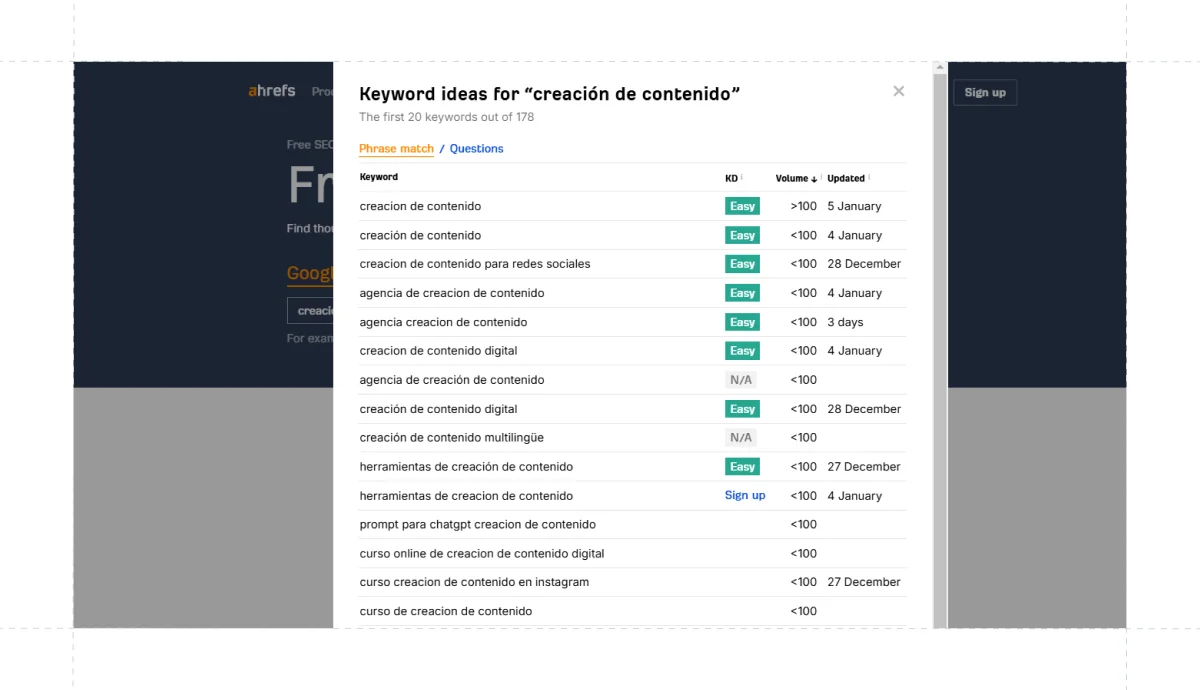
- Avoid automated translation tools – Avoid relying on tools like Google Translate, as they often make mistakes and fail to capture cultural nuances critical for SEO.
3. Choose the Right URL Structure
To create a multilingual website, you need to use dedicated URLs for each language and country version.
There are four main ways to structure URLs for multilingual sites:
- Subfolders
- Subdomains
- Separate domains
- URL parameters
Each approach comes with its pros and cons, influencing factors like SEO, user experience, and site maintenance in different ways.
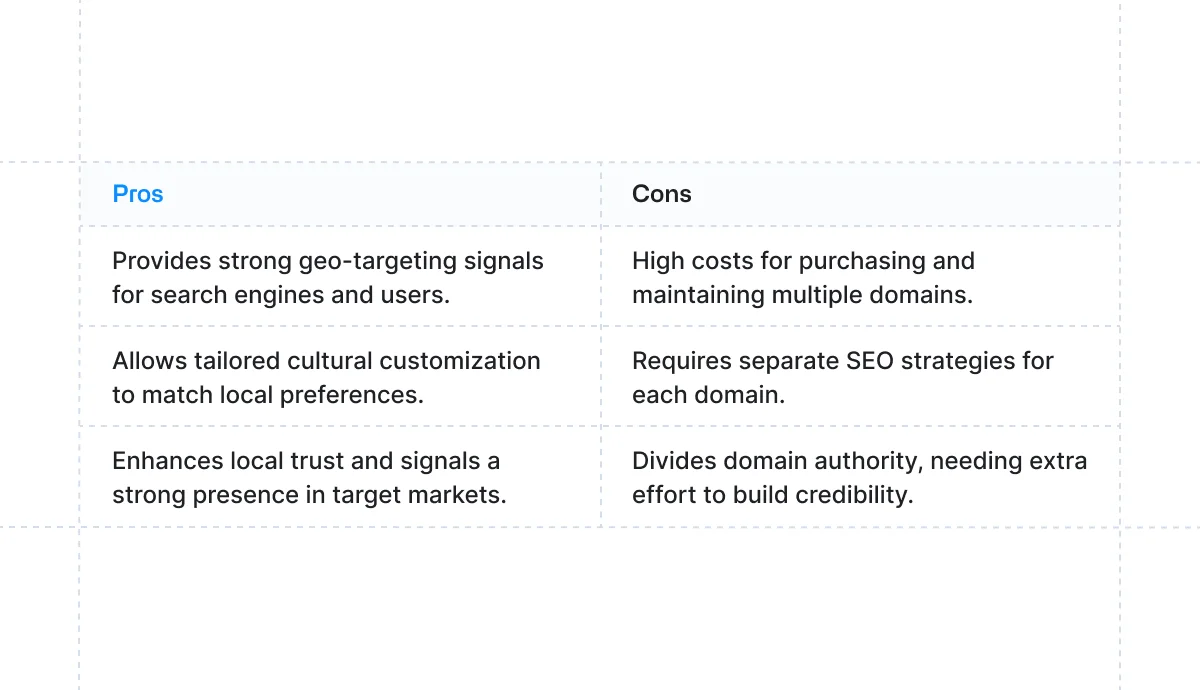
Separate Domains
Using separate domains or country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) is a widely used approach for multilingual websites.
For example:
This approach takes advantage of users’ familiarity with their country’s domain extensions. Seeing a local domain instantly reassures visitors they’re in the right place for their region.
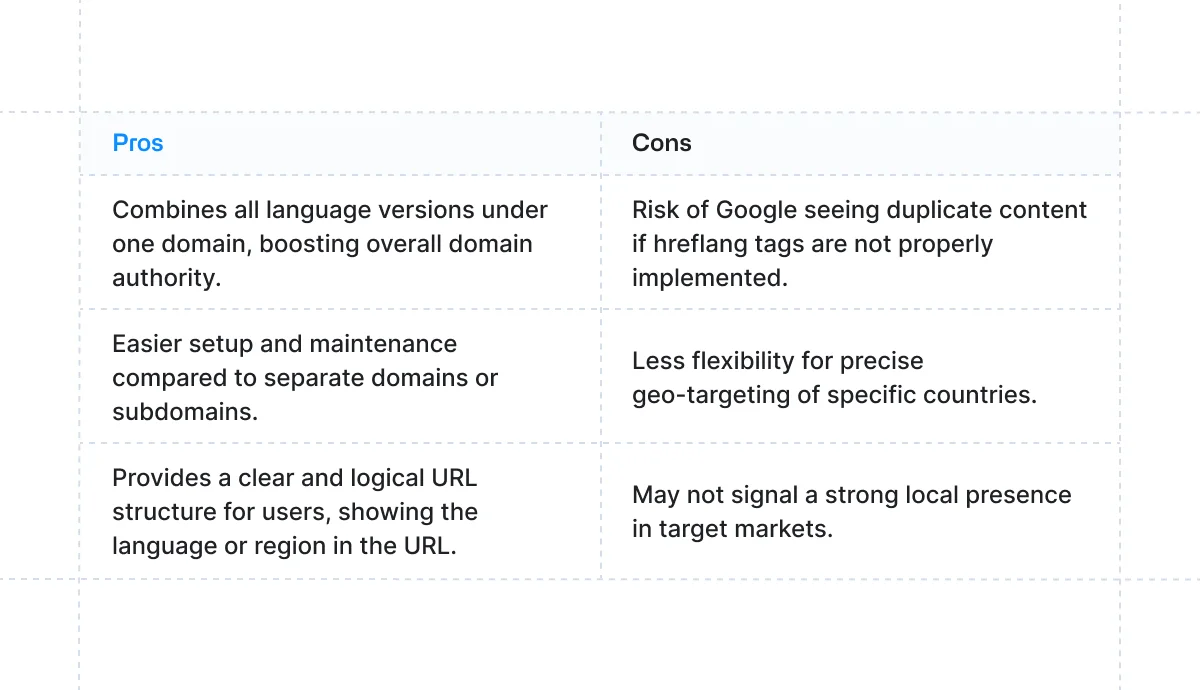
Subfolders
Using subfolders is another widely popular approach for managing websites in multiple languages.
With this method, all your content remains within a single domain, making it easier to organize and maintain.
For example:
www.wikipedia.org/en/ (English)
www.wikipedia.org/es/ (Spanish)
www.wikipedia.org/fr/ (French)
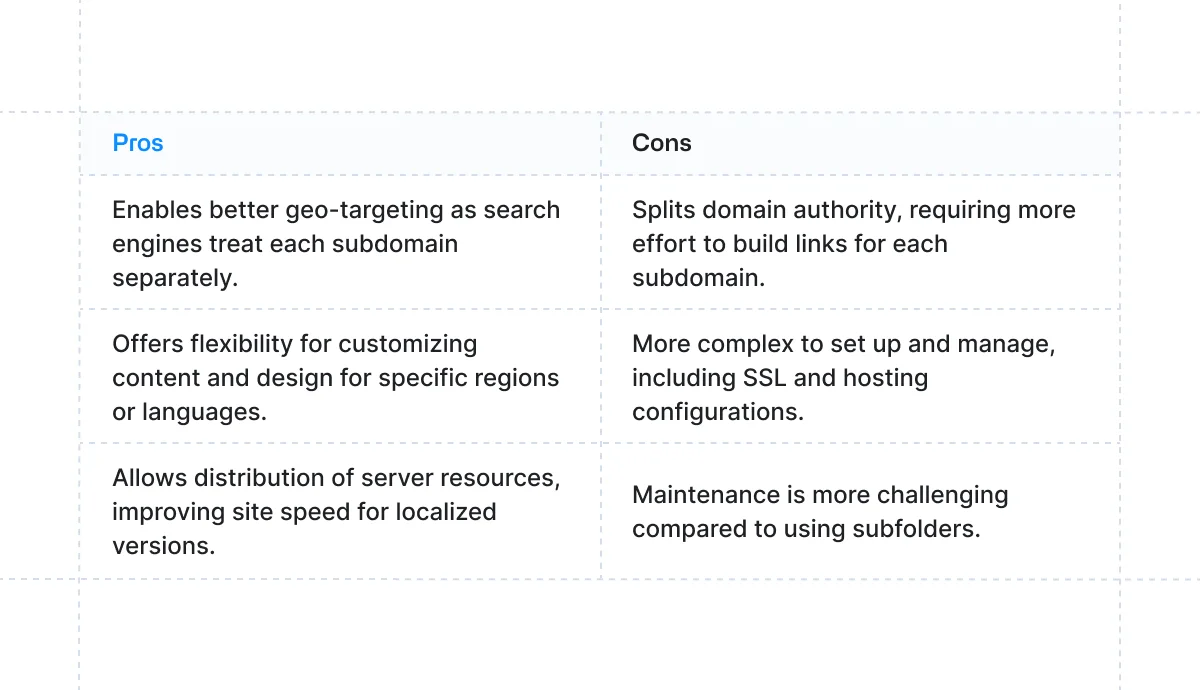
Subdomain
Subdomains are another option to consider. They work by placing the language or country code before the main domain.
For example:
- en.wikipedia.org
- es.wikipedia.org
- de.wikipedia.org
URL Parameters
Google advises against parameterized URLs for language-specific SEO as search engines might struggle to understand and display the correct language version to users.
Examples of Parameterized URLs:
- www.website.com?loc=es
- www.website.com?loc=fr
- www.website.com?loc=de
4. Translate and Optimize Your Pages
Once your URL structure is ready, translate your pages and optimize them for target keywords. While tools like Google Translate can provide a useful starting point, caution is advised as they may produce inaccurate or awkward translations, making it essential to refine the content further for the desired quality and tone.
Work with skilled human translators or use tools like Weglot to ensure natural and accurate translation.
Translate all key elements, including:
- On-page copy
- Currencies
- Time zones
- Image alt texts
While translating, optimize your pages for on-page SEO to ensure they perform well in search results.
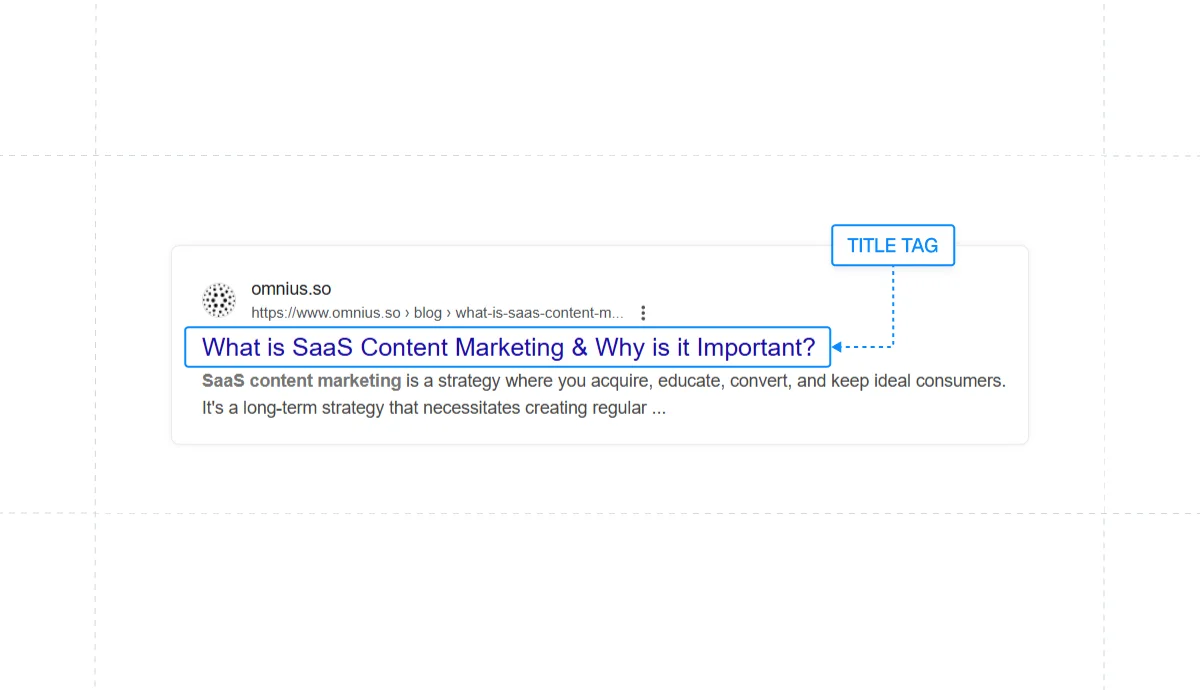
Title Tags
The title tag is often the key information people rely on when deciding which result to click.
Here’s how to create compelling title tags for your translated pages:
- Keep it short – Limit title tags to fewer than 60 characters. Google truncates anything longer, so a concise and focused title displays the entire message.
- Incorporate keywords – Include your multilingual SEO keyword in the title. This helps Google understand the page’s topic and rank it appropriately for relevant searches.
- Avoid clickbait – Ensure your title accurately reflects the page’s content. Misleading titles might attract clicks initially, but they can harm user trust and lead to higher bounce rates.
Meta Descriptions
While they don’t directly affect your search ranking, meta descriptions influence your click-through rate (CTR).

Here are some tips for crafting effective meta descriptions for translated pages:
- Keep them short – Aim for under 120 characters, as Google truncates longer descriptions.
- Include keywords – Use relevant keywords to align with search queries, as Google often highlights these in bold.
- Use active voice – Speak directly to the searcher to make your descriptions engaging and actionable.
Internal Links
Internal links are valuable for two main reasons:
- They help visitors easily navigate your site and discover more information.
- They assist Google in finding and indexing additional pages on your website.
When optimizing a multilingual website for SEO, it’s essential to create internal links between pages in the same language.
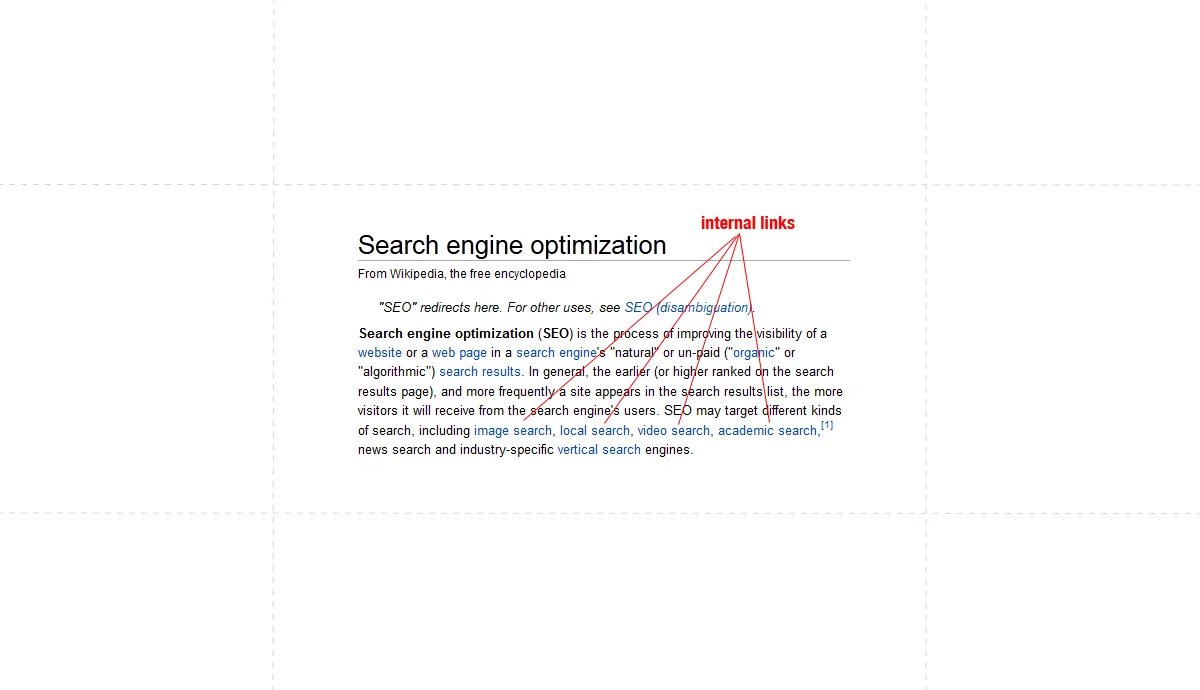
For example, Spanish pages should link to other relevant Spanish pages on your site.
This ensures a seamless user experience and helps search engines understand the structure of your content.
Url Slugs
A well-crafted URL slug helps users understand where they’ll land when clicking a link.
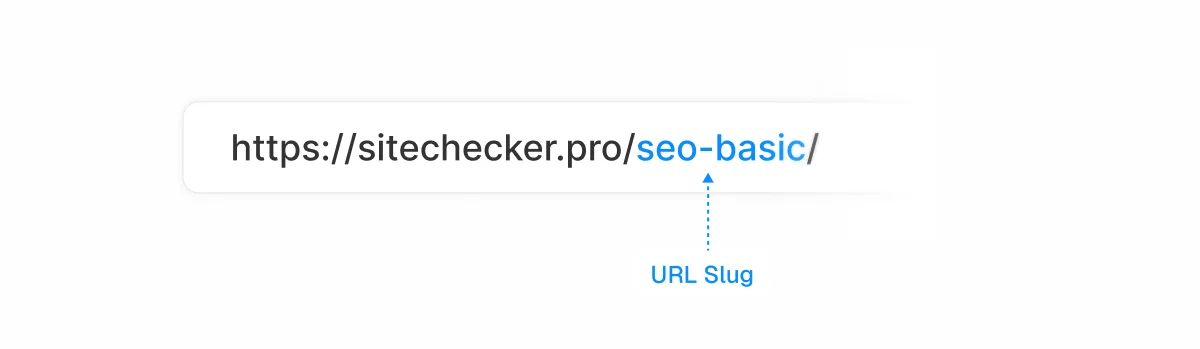
Here’s how to create effective URL slugs:
- Keep it short and descriptive.
- Always use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words.
- Stick to lowercase letters.
- Avoid special characters.
- Don’t include dates.
5. Use Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags are a helpful tool used by Google to identify both the language of a webpage and its target region.
Using these tags ensures that the correct version of your content is shown to the right audience.
Hreflang tags are included in the header section of your webpage.
Here’s an example of an hreflang tag for a Spanish-language page targeting users in Germany:
For pages translated into multiple languages, you should add several hreflang attributes covering all the languages.
For instance, if your page targets Spanish-speaking users in Germany and German-speaking users in Germany, you would include:
While this approach is effective, implementing hreflang tags can be quite complex and time-consuming, especially if you’re new to SEO, so don’t feel discouraged if it takes time to get it right.
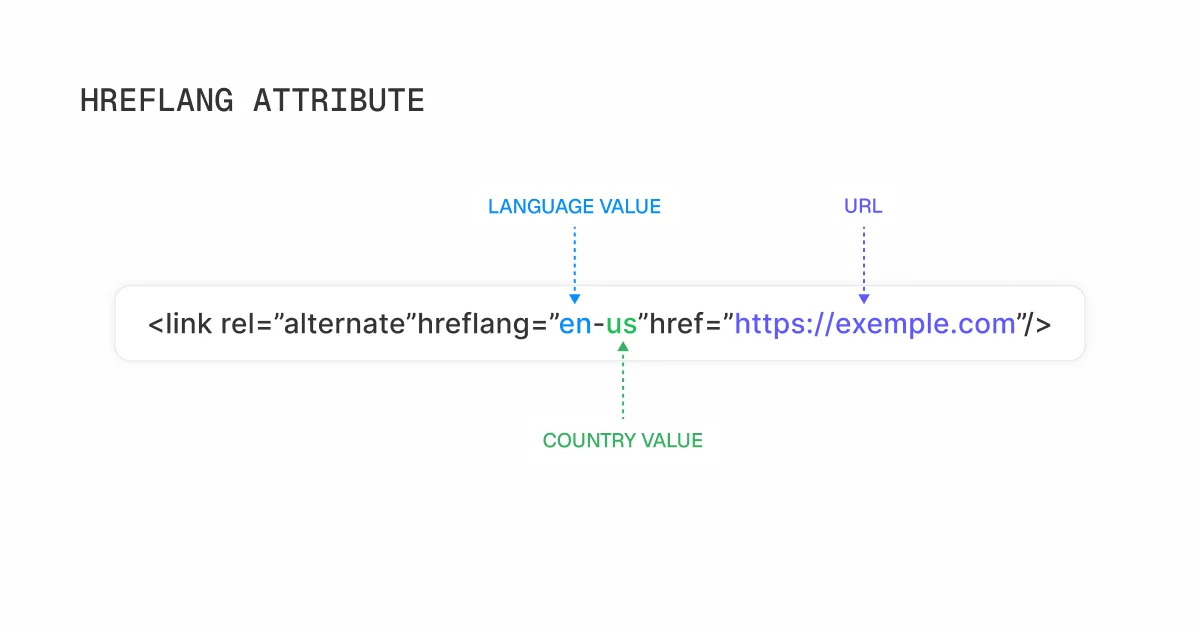
Follow these steps to implement hreflang tags:
- Decide on the method – Choose between adding the tags directly in your webpage’s section.
- Format the tags correctly – Use the proper format, including the “hreflang” attribute for language-region codes and the “href” attribute pointing to the relevant URL.
- Test your implementation – Use the Hreflang Tags Testing Tool or other SEO tools to verify your tags are correctly applied.
- Keep your sitemap updated – If you’re using an XML sitemap, ensure it’s always updated with any changes to your site’s structure or regional targeting.
6. Create a Multilingual XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a crucial tool for ensuring search engines can effectively crawl and index all language and region-specific pages on your site.
It guides search engines, detailing every URL available in different languages or targeted regions.

You can use tools like XML Sitemap Generator, Screaming Frog, or WordPress to help you create an XML sitemap
Here is how to do it in 5 steps:
Step 1: Gather Page URLs
Prepare a list of all the pages on your website, including their language variants. For example:
- English: https://example.com/page1
- Spanish: https://example.com/es/page1
Step 2: Create the Sitemap Format
Each
- The main URL
- Alternate URLs with hreflang attributes pointing to language versions
Here’s an example of how it looks for two pages in English and Spanish:

Step 3: Use ISO Language Codes
Make sure to use valid ISO 639-1 language codes.
For region-specific pages, append a country code after the language code, separated by a hyphen. For example:
- English (US): en-us
- Spanish (Spain): es-es
Step 4: Validate the Sitemap
After creating the sitemap, validate it to ensure it follows XML standards. You can use tools like Google Search Console or XML Sitemap Validator to do this.
Step 5: Submit to Search Engines
After successfully validating your XML sitemap, the next step is to make it accessible to search engines by uploading it to your website’s root directory.
Place the sitemap file in a location like “https://example.com/sitemap.xml,” ensuring it is publicly accessible for search engine crawlers.
Multilingual SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Watch out for these common mistakes when building your multilingual SEO strategy:
❌ Redirecting users automatically – Automatically redirecting users based on location or language can confuse them and restrict their access to other versions of your site.
Instead, offer a pop-up that lets users choose the version they want to visit.
❌ Using automated translation alone – Machine translations often lack context, leading to embarrassing or incorrect interpretations of your content.
Hiring professional translators ensures clarity and cultural relevance while preserving your brand image.
❌ Forgetting to translate hidden parts of the website – Visible content isn’t the only thing that needs translation. Elements like meta titles, descriptions, and error messages matter too. Overlooking these can harm your multilingual SEO and user experience.
❌ Not considering product availability – Some products may not be available in all countries due to regulations or shipping challenges.
Use IP-based redirection or display a “Not available in your area” message to improve customer experience.
❌ Forgetting to localize content – Content created for one country’s audience may not be relevant in another, even if the language is the same. Localization ensures your content feels tailored and relatable to each specific audience.
To Wrap Things Up
Now that you know multilingual SEO best practices, you’re set to take your business to the global stage.
The key is to stay consistent, adapt to cultural nuances, and ensure your website speaks directly to your target audience.
Don’t forget to stay proactive by monitoring performance, keeping up with industry trends, and adapting to changes.
If you need a team of experts to guide you, Omnius is here to help.
Book a free 30-minute call to discover how we can help reach a global audience with high-quality SEO strategies!
FAQ
How is International SEO Different from Multilingual SEO?
Multilingual SEO optimizes content for audiences speaking different languages, making it ideal for businesses targeting global markets.
International SEO, on the other hand, tailors content for specific countries, even if the language remains the same.
For example, a US company targeting the UK would use international SEO to address cultural and language variations like spelling and context.
Nguồn: omnius.so